In [12]:
plt.rc('figure', figsize=(13, 5))
balance = [np.sum(qtable.argmax(axis=-1) == i.value) for i in env.ACTION]
plt.bar(range(len(balance)), balance, tick_label=[i.name for i in env.ACTION]) and None
SNAKE_QTABLE_PATH = '/content/gdrive/MyDrive/msp430.snake.qtable.json.gz'
SNAKE_QSTORY_PATH = SNAKE_QTABLE_PATH[:31] + 'qstory.chckpnt.json'
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount(SNAKE_QTABLE_PATH[:15])
Mounted at /content/gdrive
md5 = !md5sum 'snake_game.py'
assert 'fe6f1b08c885095e7425b25c5a7ad9e5' == md5[0].split()[0]
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import copy
import json
import gzip
import hashlib
from snake_game import SnakeGame
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
env = SnakeGame()
def extract_features(game=env):
snake, food = game.get_state()
obsticle = lambda k: copy.deepcopy(game).step(k).done
o = sum(v << i for i, v in enumerate(obsticle(k) for k in game.ACTION))
a, b = snake.head.h - food.h, snake.head.w - food.w
c, d = abs(a) < env.board_height / 2, abs(b) < env.board_width / 2
a, b = (max(min(1, i), -1) + 1 for i in (a, b))
c, d = (int(i) for i in (c, d))
return o, a, b, c, d
extract_features()
(0, 0, 0, 1, 1)
Now, we'll create our Q-table, to know how much rows (states) and columns (actions) we need, we need to calculate the action_size and the state_size
def save_checkpoint(qtable, history):
data = qtable.tolist(), history
md5 = hashlib.md5(json.dumps(data).encode()).hexdigest()
with open(SNAKE_QSTORY_PATH, 'w') as f:
f.write(json.dumps([data, md5]))
!cp "$SNAKE_QSTORY_PATH" "$SNAKE_QSTORY_PATH".bak
def maybe_load_checkpoint():
for candidate in SNAKE_QSTORY_PATH, SNAKE_QSTORY_PATH + '.bak':
try:
with open(candidate, 'r') as f:
data, md5 = json.load(f)
if md5 == hashlib.md5(json.dumps(data).encode()).hexdigest():
print('Qtable and history loaded from', candidate[24:], md5)
qtable, history = data
qtable = np.array(qtable)
return qtable, history
except:
pass
print("Training from scratch")
action_space_size = len(env.ACTION)
qtable = np.random.rand(1 << action_space_size, 3, 3, 2, 2, action_space_size)
return qtable, []
qtable, history = maybe_load_checkpoint()
qtable.shape, qtable.size, len(history)
Qtable and history loaded from msp430.qstory.chckpnt.json c6ba76c6c764683f80bb8ad226b332c8
((16, 3, 3, 2, 2, 4), 2304, 2386361)
plt.rc('figure', figsize=(13, 5))
balance = [np.sum(qtable.argmax(axis=-1) == i.value) for i in env.ACTION]
plt.bar(range(len(balance)), balance, tick_label=[i.name for i in env.ACTION]) and None
ALPHA = 0.2 # Learning rate
GAMMA = 0.9 # Discounting rate
# Exploration parameters
max_epsilon = 1.0 # Exploration probability at start
min_epsilon = 0.01 # Minimum exploration probability
epsilon_decay = 1e-05 # Exponential decay rate for exploration prob
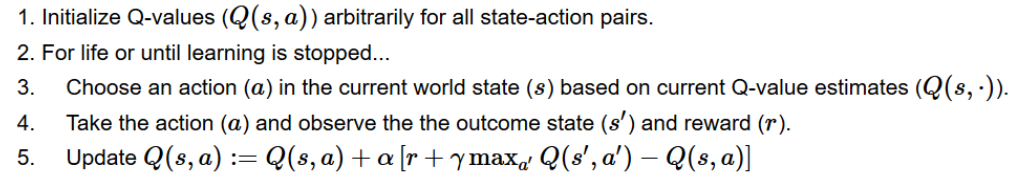
time_limit = timedelta(hours=11, minutes=50) # colab 12 hours limit
stop_time = datetime.now() + time_limit
# 2 For life or until session time expired
while datetime.now() < stop_time:
# Reset the environment
env.reset()
state = extract_features()
done = False
total_rewards = 0
total_steps = 0
# Reduce epsilon (because we need less and less exploration)
epsilon = (max_epsilon - min_epsilon) * np.exp(-epsilon_decay * len(history))
epsilon += min_epsilon
while not done:
# 3. Choose an action a in the current world state (s)
# First we randomize a number
exp_exp_tradeoff = np.random.random()
# If this number > greater than epsilon -->
# exploitation (taking the biggest Q value for this state)
if exp_exp_tradeoff > epsilon:
action = np.argmax(qtable[state])
# Else doing a random choice --> exploration
else:
action = env.random_action()
# Take the action (a) and observe the outcome state(s') and reward (r)
_, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
new_state = extract_features()
# Update Q(s,a):= Q(s,a) + lr * [R(s,a) + GAMMA * max Q(s',a') - Q(s,a)]
# qtable[new_state,:] : all the actions we can take from new state
i = state + (action,)
qtable[i] += ALPHA * (reward + GAMMA * qtable[new_state].max() - qtable[i])
total_rewards += reward
total_steps += 1
# Our new state is state
state = new_state
history.append((total_rewards, total_steps, info.score))
if len(history) % 1000 == 0:
h1k = zip(*history[-1000:])
print('\r%7d' % (len(history) // 1000),
'| Epsilon: %0.2f' % epsilon,
'| Reward: %5.2f' % np.average(next(h1k)),
'| Age: %4d' % np.average(next(h1k)),
'| Score: %4d' % np.average(next(h1k)),
'| %d %%' % (100 * (1 - (stop_time - datetime.now()) / time_limit)),
end = '')
save_checkpoint(qtable, history)
2605 | Epsilon: 0.01 | Reward: 16.57 | Age: 271 | Score: 1503 | 99 %
plt.rc('figure', figsize=(13, 4))
history = zip(*history)
plt.plot(next(history))
plt.ylabel('Rewards')
plt.xlabel('Games') and None
plt.plot(next(history))
plt.ylabel('Steps')
plt.xlabel('Games') and None
plt.plot(next(history))
plt.ylabel('Score')
plt.xlabel('Games') and None
with gzip.open(SNAKE_QTABLE_PATH, 'wt') as f:
json.dump(qtable.argmax(axis=-1).tolist(), f)
!md5sum "$SNAKE_QTABLE_PATH"
b8bc01f832c0787147ad0fddbf9c4d76 /content/gdrive/MyDrive/msp430.snake.qtable.json.gz